Two pointer algorithm is one of the basic and easy data structures for beginners. It is also commonly asked in most of the interview
In this tutorial, we will learn to apply the two pointer algorithm to find the sum of two numbers in a sorted array
Input
given sorted array
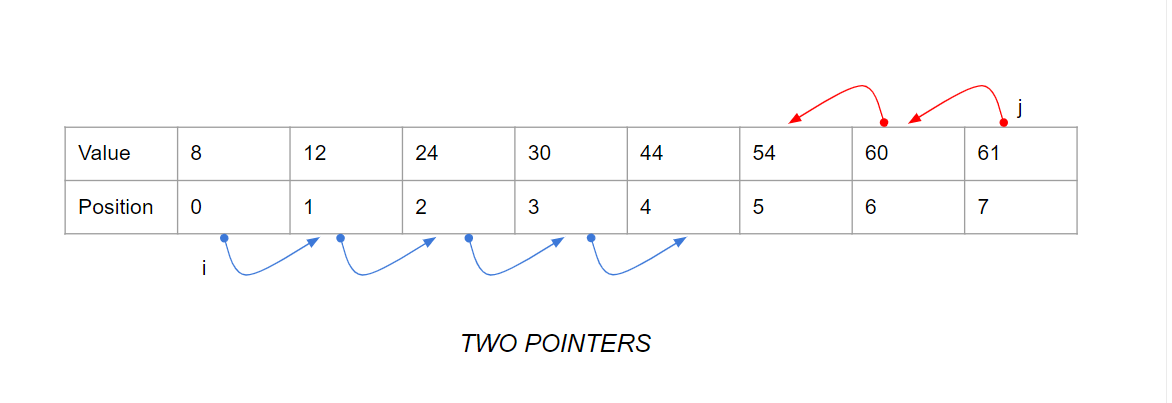
let a = {8 , 12, 24, 30, 44, 54, 60, 61}
sum of two numbers
let x = 98
Output
44,54
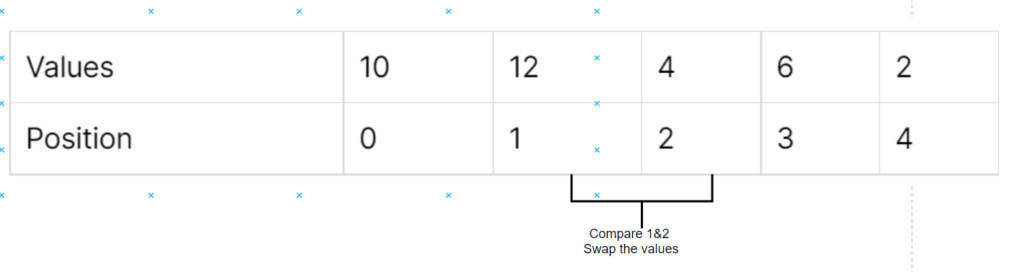
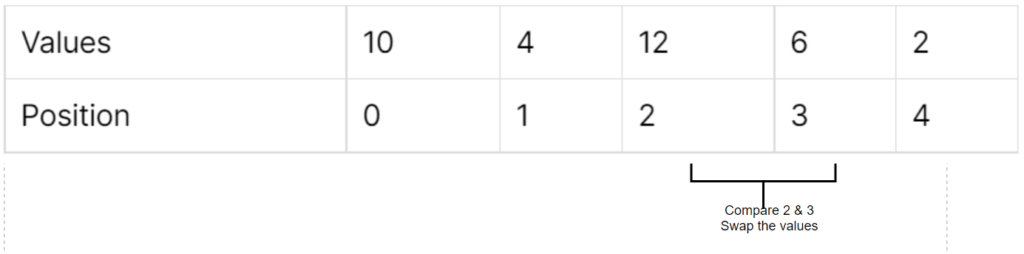
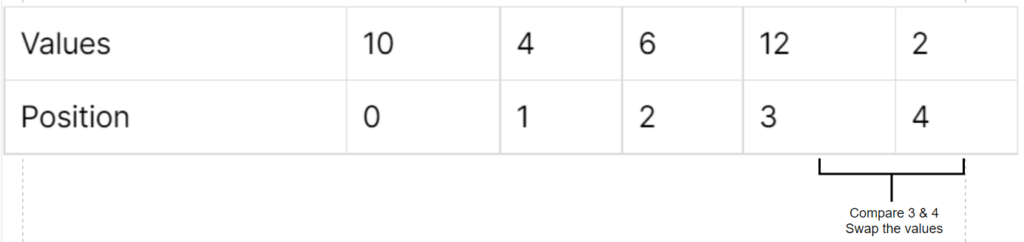
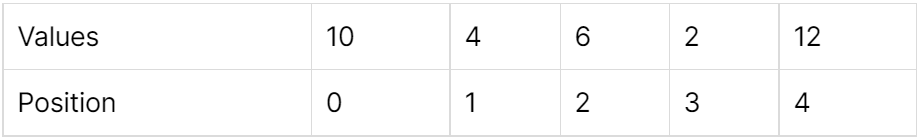
Algorithm explanation
- The Array should be Sorted in ascending
- initialize a variable as i with starting position as zero
- initialize a variable as j with starting position as n-1
- check the sum of index i & j, if matches then print the value
- else if the sum is less than the target value then increase the i position
- else decrease the j position
Example
public class TwoPointersExample {
private void sumofTwoNumbers(int a[], int x) {
if (a != null && a.length > 0) {
int i = 0;
int j = a.length - 1;
boolean isFound = false;
while (i < j) {
int sum = a[i] + a[j];
if (x == sum) {
System.out.println("The value is " + a[i] + " " + a[j]);
isFound = true;
break;
} else if (sum < x) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
if (!isFound) {
System.out.println("Not able to find with given input");
}
} else {
System.out.println("Not a valid input");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {8, 12, 24, 30, 44, 54, 60, 61};
TwoPointersExample example = new TwoPointersExample();
example.sumofTwoNumbers(a, 98);
;
}
}Output
The value is 44 54