In this post, We will learn about the selection sort algorithm in the java language. It is a comparison-based sorting algorithm
Selection sort will select the element from an array, and keep on compare with the remaining elements.
End of each iteration we will obtain the minimum value, After that we will swap the minimum element to the sorted array
Likewise, it will select all the elements in the array and compare them with the remaining element
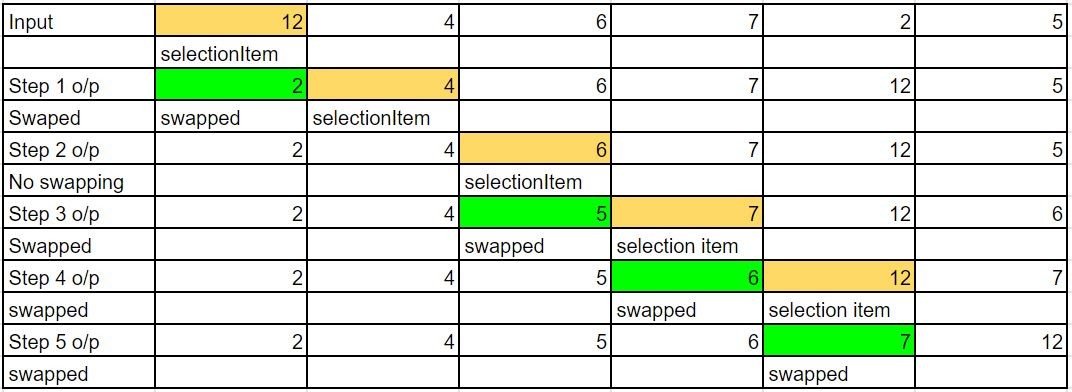
Unsorted Input array: [ 12, 4, 6, 7, 2, 5 ] Sorted Output array: [ 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 12 ]
Execution Steps
- [2, 4, 6, 7, 12, 5]
- [2, 4, 6, 7, 12, 5]
- [2, 4, 5, 7, 12, 6]
- [2, 4, 5, 6, 12, 7]
- [2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 12]
Selection Sort
Time Complexity : O(n^2)
Code
package example;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectionSort {
private void sortArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int selectionItem = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[selectionItem]) {
selectionItem = j;
}
}
int temp = arr[selectionItem];
arr[selectionItem] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 12, 4, 6, 7, 2, 5 };
SelectionSort selectionSort = new SelectionSort();
selectionSort.sortArray(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}Output
[2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 12]