In this post, We will learn about window function in pyspark with example.
What is window function ?
Window function in pyspark acts in a similar way as a group by clause in SQL.
It basically groups a set of rows based on the particular column and performs some aggregating function over the group.
Sample program for creating dataframe
For understanding the concept better, we will create a dataframe containing the salary details of some employees using the below program.
# Creating dictionary with employee and their salary details
dict1=[{"Emp_id" : 123 , "Dep_name" : "Computer" , "Salary" : 2500 } , {"Emp_id" : 456 ,"Dep_name" :"Economy" , "Salary" : 4500} , {"Emp_id" : 789 , "Dep_name" : "History" , "Salary" : 6700 } , {"Emp_id" : 564 , "Dep_name" : "Computer" , "Salary" : 1400 } , {"Emp_id" : 987 , "Dep_name" : "History" , "Salary" : 3450 }, {"Emp_id" :678 , "Dep_name" :"Economy" ,"Salary": 6700}]
# Creating RDD from the dictionary created above
rdd1=sc.parallelize(dict1)
# Converting RDD to dataframe
df1=rdd1.toDF()
print("Printing the dataframe df1")
df1.show()Printing the dataframe df1
+--------+------+------+
|Dep_name|Emp_id|Salary|
+--------+------+------+
|Computer| 123| 2500|
| Economy| 456| 4500|
| History| 789| 6700|
|Computer| 564| 1400|
| History| 987| 3450|
| Economy| 678| 6700|
+--------+------+------+How to use window function in our program?
In the below segment of code, the window function used to get the sum of the salaries over each department.
The following library is required before executing the code.
from pyspark.sql import Window
partitionBy includes the column name based on which the grouping needs to be done.
df = df1.withColumn("Sum",sum('Salary').over(Window.partitionBy('Dep_name')))
print("Printing the result")
df.show()Printing the result +--------+------+------+-----+ |Dep_name|Emp_id|Salary| Sum| +--------+------+------+-----+ |Computer| 123| 2500| 3900| |Computer| 564| 1400| 3900| | History| 789| 6700|10150| | History| 987| 3450|10150| | Economy| 456| 4500|11200| | Economy| 678| 6700|11200| +--------+------+------+-----+
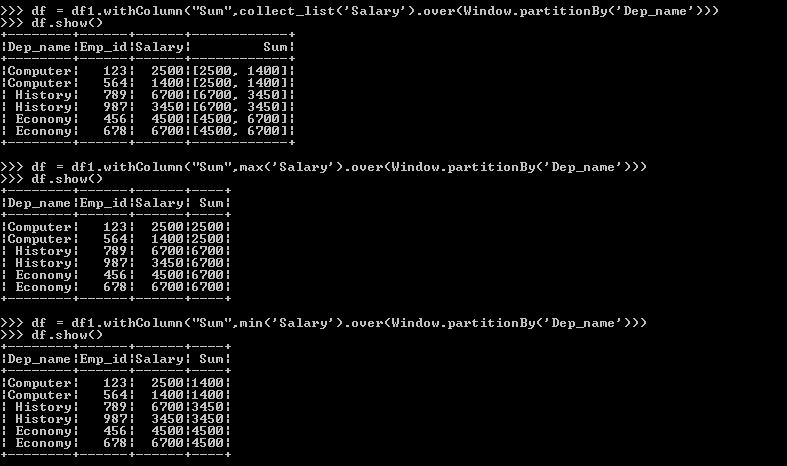
Other aggregate functions
As above, we can do for all the other aggregate functions also. Some of those aggregate functions are max(),Avg(),min(),collect_list().
Below are the few examples of those aggregate functions.
Reference
https://medium.com/@rbahaguejr/window-function-on-pyspark-17cc774b833a
Related Articles
Window function in pyspark with example using advanced aggregate functions like row_number(), rank(),dense_rank() can be discussed in our other blogs .


