In this post, Let us know rank and dense rank in pyspark dataframe using window function with examples.
Rank and dense rank
The rank and dense rank in pyspark dataframe help us to rank the records based on a particular column.
This works in a similar manner as the row number function .To understand the row number function in better, please refer below link.
The row number function will work well on the columns having non-unique values . Whereas rank and dense rank help us to deal with the unique values.
Sample program – creating dataframe
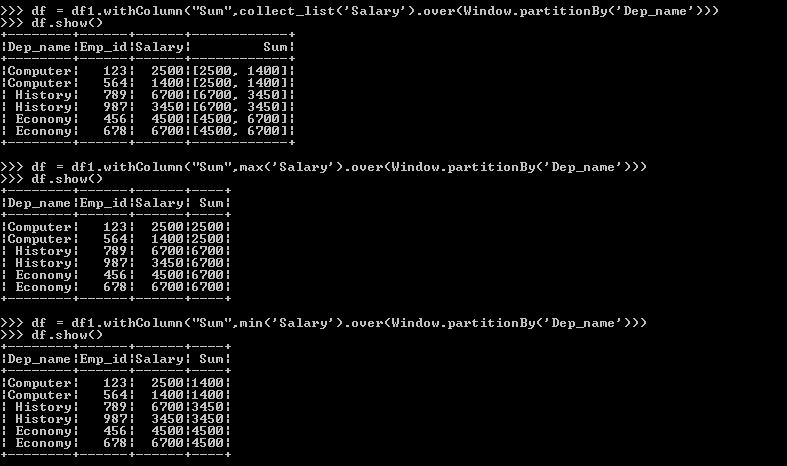
We could create the dataframe containing the salary details of some employees from different departments using the below program.
from pyspark.sql import Row
# Creating dictionary with employee and their salary details
dict1=[{"Emp_id" : 123 , "Dep_name" : "Computer" , "Salary" : 2500 } , {"Emp_id" : 456 ,"Dep_name" :"Economy" , "Salary" : 4500} , {"Emp_id" : 789 , "Dep_name" : "Economy" , "Salary" : 7200 } , {"Emp_id" : 564 , "Dep_name" : "Computer" , "Salary" : 1400 } , {"Emp_id" : 987 , "Dep_name" : "History" , "Salary" : 3450 }, {"Emp_id" :678 , "Dep_name" :"Economy" ,"Salary": 4500},{"Emp_id" : 943 , "Dep_name" : "Computer" , "Salary" : 3200 }]
# Creating RDD from the dictionary created above
rdd1=sc.parallelize(dict1)
# Converting RDD to dataframe
df1=rdd1.toDF()
print("Printing the dataframe df1")
df1.show()Printing the dataframe df1
+--------+------+------+
|Dep_name|Emp_id|Salary|
+--------+------+------+
|Computer| 123| 2500|
| Economy| 456| 4500|
| Economy| 789| 7200|
|Computer| 564| 1400|
| History| 987| 3450|
| Economy| 678| 4500|
|Computer| 943| 3200|
+--------+------+------+Sample program – rank()
In order to use the rank and dense rank in our program, we require below libraries.
from pyspark.sql import Window
from pyspark.sql.functions import rank,dense_rank
from pyspark.sql import Window
from pyspark.sql.functions import rank
df2=df1.withColumn("rank",rank().over(Window.partitionBy("Dep_name").orderBy("Salary")))
print("Printing the dataframe df2")
df2.show()
In the below output, the department economy contains two employees with the first rank. This is because of the same salary being provided for both employees.
But instead of assigning the next salary with the second rank, it is assigned with the third rank. This is how the rank function will work by skipping the ranking order.
Printing the dataframe df2
+--------+------+------+----+
|Dep_name|Emp_id|Salary|rank|
+--------+------+------+----+
|Computer| 564| 1400| 1|
|Computer| 123| 2500| 2|
|Computer| 943| 3200| 3|
| History| 987| 3450| 1|
| Economy| 456| 4500| 1|
| Economy| 678| 4500| 1|
| Economy| 789| 7200| 3|
+--------+------+------+----+Sample program – dense rank()
In the dense rank, we can skip the ranking order . For the same scenario discussed earlier, the second rank is assigned in this case instead of skipping the sequence order.
from pyspark.sql import Window
from pyspark.sql.functions import dense_rank
df3=df1.withColumn("denserank",dense_rank().over(Window.partitionBy("Dep_name").orderBy("Salary")))
print("Printing the dataframe df3")
df3.show()Printing the dataframe df3
+--------+------+------+---------+
|Dep_name|Emp_id|Salary|denserank|
+--------+------+------+---------+
|Computer| 564| 1400| 1|
|Computer| 123| 2500| 2|
|Computer| 943| 3200| 3|
| History| 987| 3450| 1|
| Economy| 456| 4500| 1|
| Economy| 678| 4500| 1|
| Economy| 789| 7200| 2|
+--------+------+------+---------+